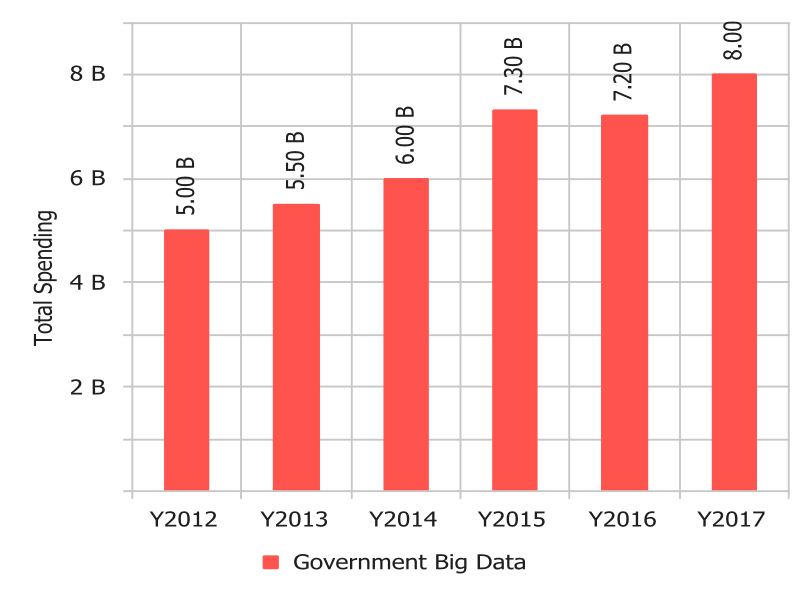
While many corporate executives initially dismissed the buzz surrounding Big Data as nothing more than hype, a seismic shift in perception is taking place.
In today’s global, rapidly evolving marketplace, leading organizations are recognizing the value of Big Data and its major role in an enterprise’s ability to stay one step ahead of the competition. As a result, enterprises are creating new business models, with a fundamentally rethinking of their approach to data center architecture and management. Companies that don’t keep up with the changing business landscape are simply being left behind.
Data, The Next Generation: The rise of Big Data is causing businesses to reevaluate how they operate.
Analytics as a Service
For years, enterprises have collected and stored data. However traditional on-premise solutions are often complex, costly and inflexible, making it difficult for enterprises to keep up with the exploding demand for real time actionable information.
With the tidal wave of information that can be converted into useful insights, today’s companies are pursuing ways to not only store massive amounts of data but to also lay the infrastructure required to perform analytics on it. The trouble is that the task is both time- and resource-intensive. For organizations that can’t afford to invest in servers to handle Big Data workloads, tapping into the cloud has become a valid alternative to maintaining a costly infrastructure.
Major Benefits of the Cloud
Cloud solutions make the most of storage resources. While the average physical server works at 12 to 18% capacity, using private cloud can raise utilization to 50%. Multi-tenancy in the public cloud can boost capacity to 80% because different organizations experience heightened data traffic at different times.
Instead of expanding on-site storage to accommodate for Big Data growth, organizations can today take advantage of Analytics-as-a-Service (AaaS) by migrating their data warehouse to the cloud.
Child’s Play? – While cloud models can be extremely complex, their implementation can save an organization from having to spend on new servers, network infrastructure or expensive software titles.
Simultaneous to the growth of Big Data, cloud technology has matured to the point where it is now addressing barriers to adoption with improvements in security and data integration – resulting in a growing number of IT organizations supporting cloud services delivery.
High-Performing Data Warehouse As-A-Service
The concept of analytics on the cloud as-a-service is enabling companies such as SQream Technologies that is exploiting thousands of compute cores concurrently, to provide organizations with real-time analytics from massively scaling data sets. SQream’s ZBDB service doesn’t require time consuming indexing or lengthy integration periods. With a seamless integration and noticeable simplicity, ZBDB makes it possible for businesses to rapidly set up, load and query their data.
ZBDB is SQream’s response to the growing demand for ‘on-demand’ computing that enables ubiquitous access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources.
A Cloud for Every Enterprise – Cloud Models
There are different deployment models available for different business structures.
Choosing a public, private or hybrid cloud depends on the types of workloads and compliance regulations an organization faces.
- Public Cloud: A computing model in which a service provider makes resources available to the general public over the Internet. Public cloud services may be free or offered on a pay-per-usage basis.
- Private Cloud: This deployment model allows a business to retain control over its data, providing greater security if needed in order to comply with privacy regulations.
- Hybrid Cloud: A cloud computing environment in which a business can keep sensitive data in-house and use the public cloud for short-term Big Data projects or accessing external data.
Conclusion
In this age of Big Data, companies that haven’t adopted cloud services may want to overcome their reservations. Gigaom Research reported that more that 53% of large enterprises are using or plan to use cloud resources for Big Data analytics.
However, getting this kind of capability may not be easy for some companies. This is where flexible cloud delivery models can, in addition to important cost savings, simplify useful insights that could provide different kinds of competitive advantages.